Insight Focus
- Sugar beet sowing is delayed in parts of the EU following heavy rainfall.
- Cold weather in some US sugar beet states has led to delays there too.
- Late sowing can have detrimental effects on yields.
Sugar beet sowing in the EU/UK and the US for their 2023/24 campaigns have been severely delayed by abnormal weather over the last few months. This opens up their crops to a number of different risk factors.
Should the late slowing have a knock-on effect on either region’s production, more imports would likely be necessary to meet domestic consumption, with both regions having duty free access for a number of the same origin countries.
Heavy Rainfall for Many EU/UK Growers
Amongst the major beet producers, the EU Joint Research Centre highlights Germany, and the UK as most extensively affected by heavy rains, with parts of France and Poland also recipients of high precipitation.
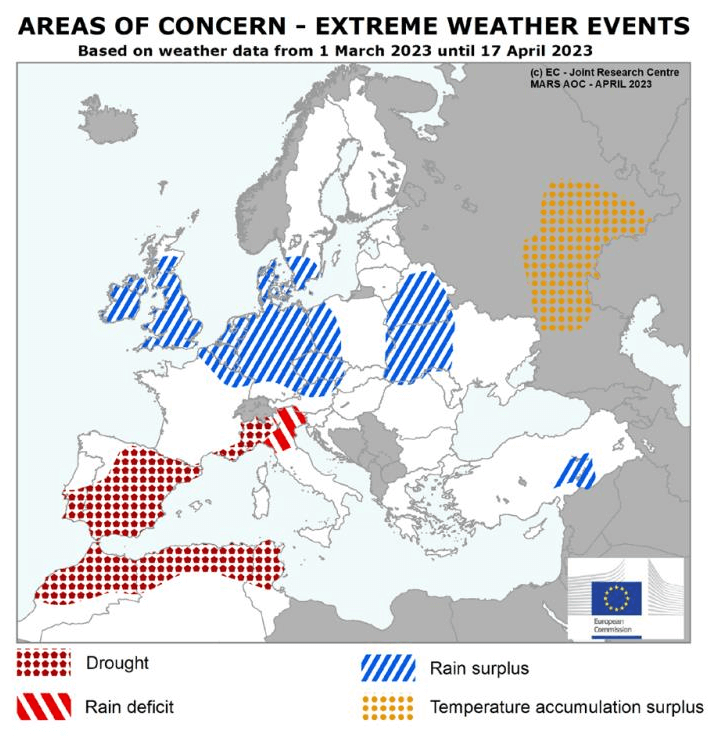
Source: JRC MARS
Late sowing leaves the crop more vulnerable to Beet Yellows Virus (BYV) as the aphids that carried it will arrive when the crop is less well established.
This is particularly relevant for growers in France who aren’t able to use neonicotinoid pesticides from this season and are reporting aphids arriving sooner than expected too.
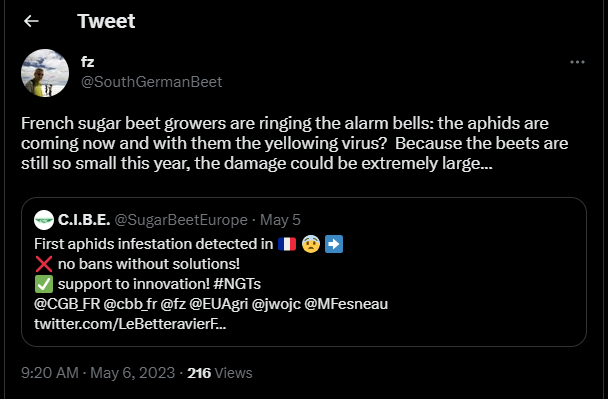
Source: CIBE
Losses from BYV were particularly severe the last time French growers were impacted back in the 2020/21 season.
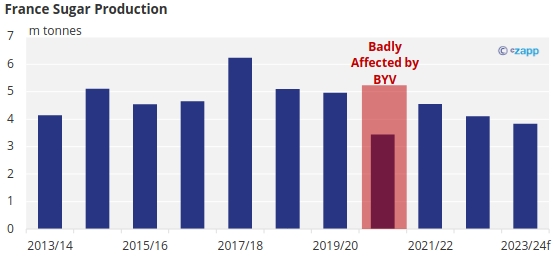
Late sowing can also lead to yield losses if the length of the growing season becomes shorter than usual.
All the above, alongside early forecasts predicting similarly hot, dry conditions to last season this summer, means there is plenty of downside risk to our 16.6m tonne forecast for EU and UK sugar production in 2023/24.
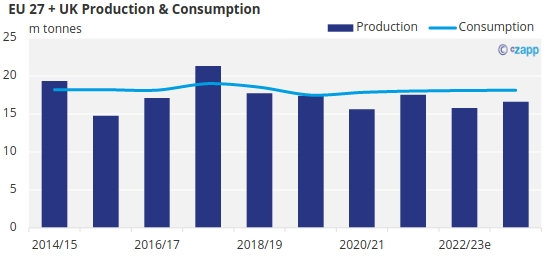
Any downside will likely manifest in a greater need for world market imports.
Cold, Snowy Conditions in the US
Colder conditions coupled with heavier-than-normal snow has meant the soil is not available for sowing for US beet farmers too.
According to the USDA, by the end of the first week of May the main sugar producing states Idaho, Michigan, North Dakota and Minnesota have only managed to plant half of their intended area.
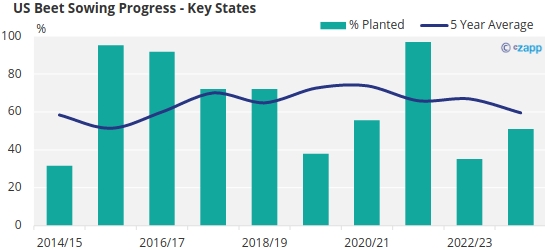
Source: USDA
This is around 10% below the 5-year average, and almost 50% below the 2021/22 season.
As with Europe, late sowing can risk lower yields, however this time last year sowing progress was the second slowest in a decade yet the 2022/23 season has ended up being the one of the largest on record. Therefore, it is still far too early to judge whether it could have any meaningful effect.
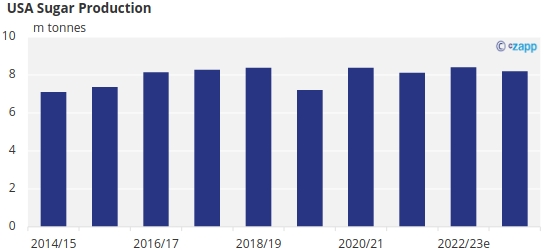
Should late sowing ultimately have a detrimental effect on US sugar production, Mexico and the TRQ origins will likely need to step up to meet any extra shortfall.










