Opinions Focus
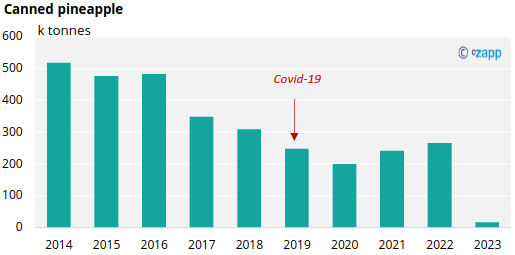
- Thailand supplies half of the world’s canned pineapple.
- Most of this is shipped to the USA and EU.
- Pineapple can also be eaten fresh, dried, as juice concentrate or jam.
Thai Pineapple Background
Although pineapple was originally indigenous to South America, Thailand is now one of the largest producers and exporters of pineapple in the world.
It’s been a major pineapple exporter since the 17th century, when farmers struggled with oversupply of fresh pineapples. The introduction of canning changed the export profile, allowing the fruit’s lifespan to be prolonged through preservation. Today, Thailand accounts for 50% of the world’s canned pineapple production, followed by Indonesia and the Philippines.
Today, 90% of the pineapple crop is exported, primarily to the USA and EU. The remainder is sold locally.
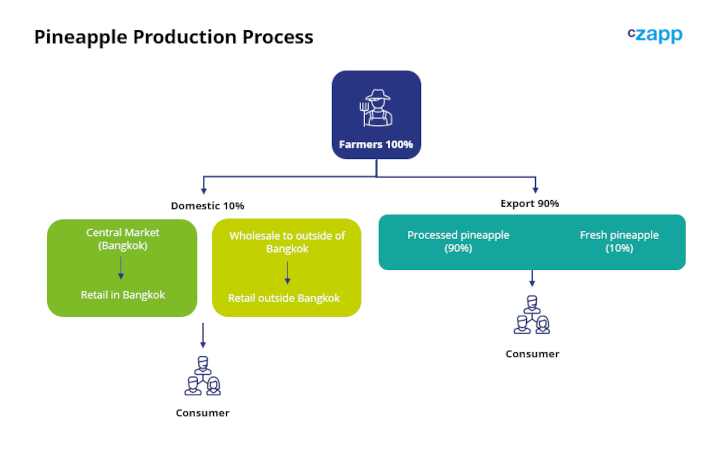
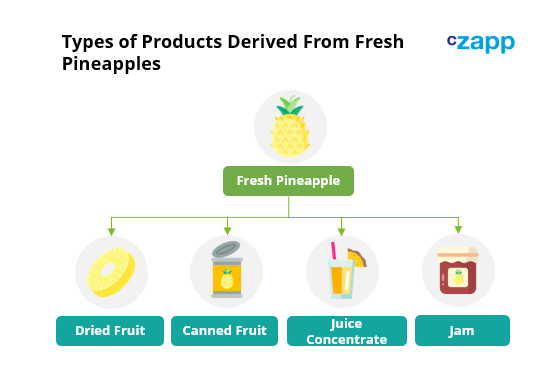
Pineapple Products
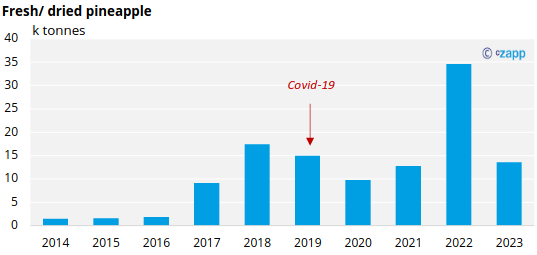
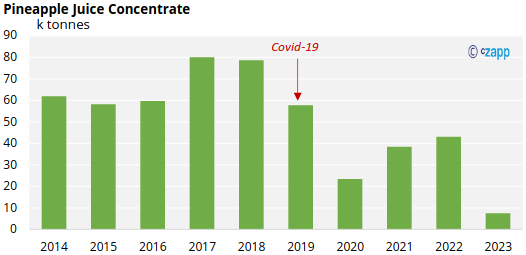
In Thailand, pineapple can be sold in various kinds of products. It can be processed into canned pineapple (juice concentrate, dice, chunk, and fine crushed), eaten as fresh or dried fruit or made into jam.
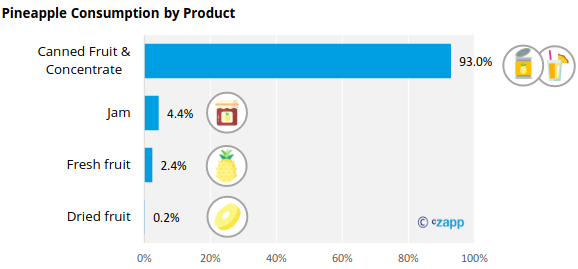
Pineapple Consumption
Thai pineapple consumption is dominated by canned fruit and concentrate, accounting for 93% of total consumption. The remaining share is distributed to jam (4.4%), fresh fruit 2.4% and dried fruit (0.2%).
Thailand’s Historical Pineapple Production
Pineapple grows as a perennial shrub around 1.5m tall. Each plant produces up to 200 flowers, with pollination under cultivation often done by hand to preserve fruit quality. Each flower of the shrub then produces a fruit, but these individual fruits mature into a single mass: the pineapple.
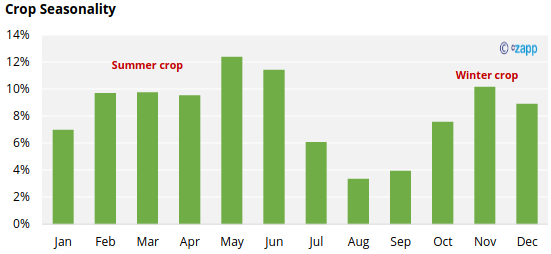
Early harvesting of the main fruit can encourage a second crop of smaller fruits. Therefore, there are two pineapple seasons in Thailand: a summer crop (February to June) and winter crop (October to December).
Pineapple harvesting area has declined slightly since 2021, mainly in the North and Central regions.
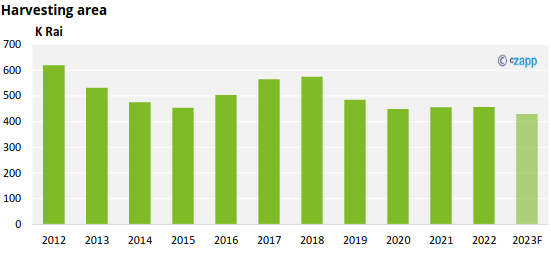
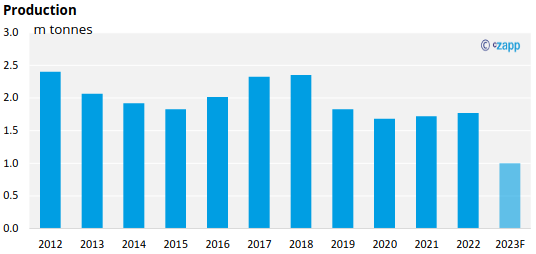
Pineapple farming and processing has been impacted by labour shortages, high fertilizer prices, and high production costs since COVID-19 pandemic. Farmers have therefore in some cases switched to growing lower-cost crops.
There are about 18 provinces in Thailand that grow pineapple.
Pineapple Production Area Map
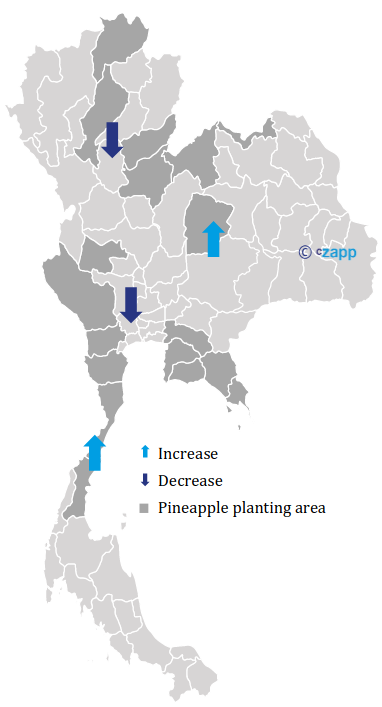
The main area for planting pineapple is Prachuap Khiri khan province at 37% of the total area, followed by Ratchaburi province at 9% and Phetchaburi province at 6%.
Pineapple Variety grown in Thailand
The pineapple cultivar in Thailand can be varied. Some can be consumed directly as a fresh fruit (for example queen pineapple). Some cultivars can be consumed in a processed form such as canned fruit, juice, concentrate etc.
Fresh Pineapple: Queen pineapple such as Phuket pineapple, Phulae pineapple, MD2, Trad Seethong etc.

Processing Pineapple: Commonly known as Pattavia pineapple in Thai or Smooth Cayenne in English. This is now the world’s dominant pineapple cultivar.

Historical Pineapple Production Cost
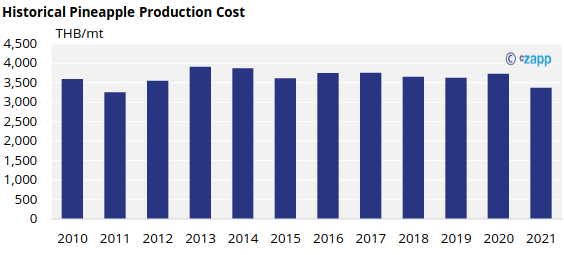
The pineapple production cost was stable between 2015 and 2021. The farmers have been impacted by labour shortage and high fertilizer prices since COVID-19 pandemic causing the production number to decline and farmers decided to apply less fertilizer to eases their cost of production until today.
Historical Domestic Price
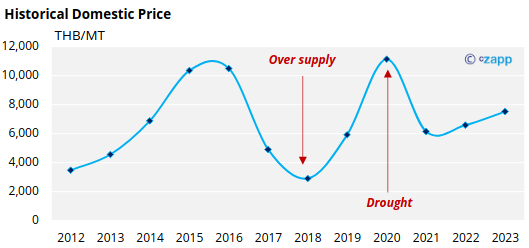
The pineapple price decreased in 2017 due to oversupply of fresh pineapple production and rose again during drought and low supply in 2020.
The following year some farmers switched to a more beneficial crop than pineapple, some processors reduced their capacity due to labour shortages and low export orders.
Historical Pineapple Export Volume