Insight Focus
China is on track to maintain its position as a key player in the citric acid export market in 2024. However, demand remains weak due to surplus inventory in key importing countries. Cutting costs and investing in R&D is high priority for producers.
Citric Acid Basics
Citric acid is a colourless weak acid that naturally occurs in citrus fruits. There are synthetic versions, which are created from cultures of Aspergillus niger and sugar.
In food and beverages, citric acid is used as a flavouring agent due to its acidic and sour taste. It’s also a preservative that’s useful in canned fruits and vegetables to protect against bacteria such as botulism.
It increases the shelf life of pre-ready foods and as a result it is used as a dry alternative to lemon juice or vinegar, in the form of seasoning salts and flavouring powders. It is also used in fertilisers to lower the PH levels of the soil.
Market demand sets the price of citric acid. Demand for soft drinks, candies, baked foods and convenience foods has propelled market growth over the years. Growth has also been driven by demand in the pharmaceutical industry and there is increased usage of citric acid in household cleaning products, such as detergents, dish soap and rust remover.
China Dominates Citric Acid Market
China accounts for approximately 70% of the citric acid market. Within the first quarter of 2024, China had exported 304,800 tonnes of citric acid. We expect China’s overall production to be at least 1.2 million tonnes by end of 2024 – a similar level to last year’s final export volume.
China sold so much citric acid to Europe prior to 2008 that an anti-dumping investigation was opened by the European Commission. In 2021, the European Union imposed anti-dumping duties on imports of citric acid from China and Malaysia at levels ranging from 6.6% to 42.7%. Nonetheless, China has managed to remain a key player in the industry, and Europe is still one of its top sales destinations.
The top five exporters globally of citric acid have not changed over the past few years.
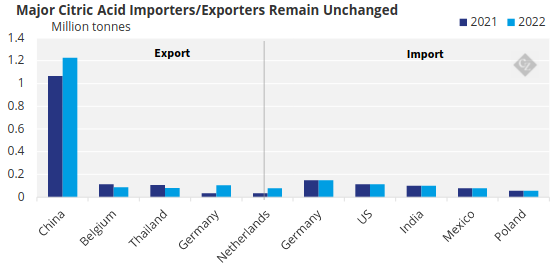
Source: WITS Global Trade
Industrial, Consumer Demand Weakens
However, demand for some Chinese citric acid is weak this year compared to last year. Prices have been low for more than six months, indicating that global demand hasn’t risen.
The reason for this weak demand is rooted in economic uncertainty. Consumer industries such as food, beverages and household cleaning are highly dependent on strong consumer demand. However, in most countries, buying activity has been subdued as food prices rise.
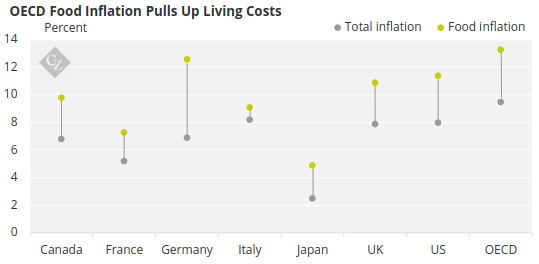
Source: OECD
Due to this lagging demand, citric acid stocks in key markets like the US and Germany remain high. This means that buyers are reluctant to purchase more, particularly given relatively high prices.
The US is a major citric acid importer and, despite increased tensions with China, it is still heavily reliant on the Asian country. Chinese New Year caused delays and Red Sea tensions led to an increase in freight costs, meaning citric acid prices rose for buyers at the beginning of the year.
However, there was a drop in prices at the end of the quarter due to stock clearing for year end. Overall, there has been a global decline in prices and a weakening in demand.
As this weak demand persists, Chinese producers are facing challenges in the form of higher production costs due to unfavourable weather, fluctuations in currency exchange rates, trade agreements and geopolitical risk.
Producers Face Fierce Competition
Citric acid is relatively easy to produce. However, this draws in new players to the market forcing the established citric acid producers to reduce their prices, which impacts profit margins and sales volumes.
As China is the top producer and exporter of citric acid, producers have been cutting costs to maintain their market share. Chinese producers have maintained their quality due to established protocols and practises in places. Additionally, as citric acid is used across a range of products, there are many investment opportunities.
The fermentation technology used for citric acid has been used for many years, but factories are now reducing production costs with greater automation, reducing personnel costs, and improving the conversion rate of citric acid to reduce raw material costs.
There have been new, exotic drinks entering the beverages market, requiring citric acid to improve shelf-life, pH buffering and providing flavour and tartness higher than other acids. This demand for ready-to-drink (RTD) healthy and soft drinks has increased R&D activity among citric acid producers.
There have been introductions of mineral blends of citric acid, offering an enhanced product. In June 2022, Jungbunzlauer introduced a monobasic magnesium salt, which is ideal for mineral beverage powders and aims to increase nutritional benefits in foods and beverages.
Looking Ahead
- Citric acid is a key component in many foods, drinks and pharmaceuticals but global demand is low due to surplus inventory in key importing countries.
- For Chinese producers, the sustained low price has been a challenge. This has pushed the focus onto reducing production costs and increasing innovation.
- R&D within citric acid promises innovative, new products which are organic and clean.
- Chinese producers are continuing production and on target to reach an estimated 1.2million kg of exported citric acid in 2024.













